What is C Rating in Lithium Battery?
The c rate is commonly used to calculate a battery’s charge and discharge rate. The c rate is a standard used to determine the magnitude of the battery charge and discharge current, as well as to anticipate the battery charge and discharge time.
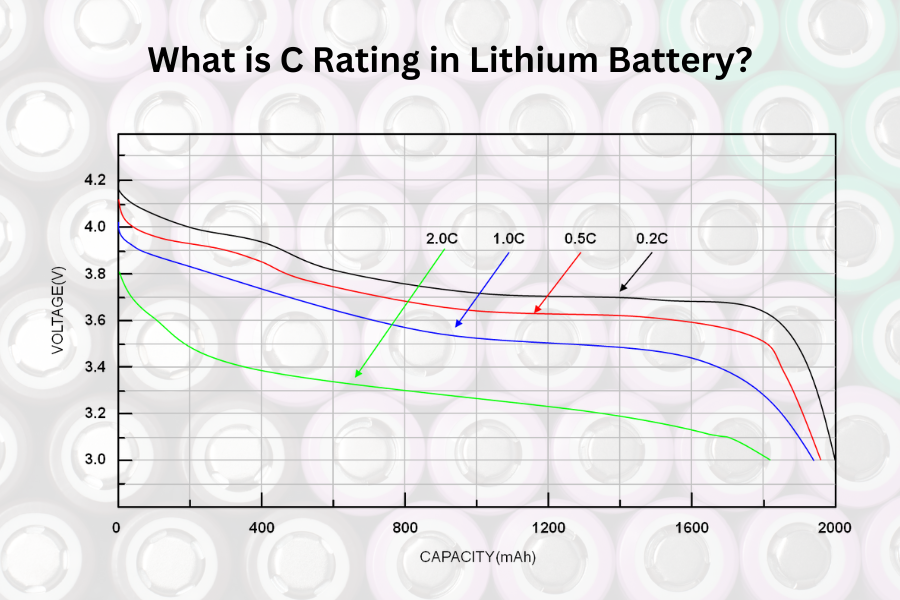
Depending on the battery type and the application environment, different batteries have varied c rates; the majority of batteries are rated at 0.2C. That is, a 1000mAh battery discharged at a 0.2c rate for five hours would produce 1000mA. A similar type of battery discharging at 0.5C would provide 500mA for 120 minutes.
In layman’s terms, it shows the battery’s charge and discharge rates. A battery with a c rate is divided into two rates: discharge and charge. The purpose of the c rate battery is to specify how long it takes for a battery to drain after it has been fully charged. A 10 C battery will discharge in 6 minutes, a 2 C battery in 30 minutes, and a 1 C battery in 60 minutes.
C rating on a lithium battery
A lithium-ion battery’s C rating is an important characteristic that influences its performance in high-drain applications such as electric automobiles, power tools, and drones. A higher C rating indicates that the battery can supply more current and power, making it appropriate for high-performance applications requiring rapid acceleration or continuous power output.
How to calculate C rating of Lithium Batteries?
To calculate a lithium-ion battery’s maximum discharge current, you must first know its capacity (C), rated voltage (V), and C rating (C). The following is the formula:
Capacity (C) x C Rating (C) / Rated Voltage (V) = Maximum Discharge Current
Take, for example, a 200Ah lithium-ion battery with a 2C rating and a rated voltage of 51.2V. The maximum discharge current is:
Maximum Discharge Current = 200Ah multiplied by 2 / 51.2V = 78.125A
This means that the battery can deliver a maximum current of 78.125A without being damaged or having its lifespan reduced.
A higher c-rated battery allows the battery to operate with less voltage drop. When the battery’s voltage can withstand greater voltages, the current rate must likewise double.
Varied application scenarios have varied battery c rate needs. Power batteries that must drive motors have greater c-rate requirements, whereas energy storage batteries used in solar energy storage systems prioritize battery capacity requirements.
Factors affecting C Rating of the batteries
The impact of the ambient temperature limits the majority of lithium-ion18650 c rate. Temperatures that are too high or too low will have an effect on the battery’s c rate. If the battery is exposed to high temperatures for an extended period of time, its cycle life may be reduced. Furthermore, if the temperature is too low, the battery c rate will suffer. The following are the primary factors influencing battery c rate:
- Temperature: Lithium-ion batteries are temperature sensitive, and extreme heat or cold can degrade their performance. High temperatures can raise the internal resistance of the battery, diminish its capacity, and shorten its cycle life. Low temperatures, on the other hand, might reduce the discharge rate of the battery and increase its internal resistance, lowering its overall performance. As a result, it’s critical to select a battery with a C rating appropriate for the application’s temperature range.
- State of Charge: A lithium-ion battery’s C rating can also vary based on its state of charge (SOC). Because of its higher voltage, a fully charged battery can supply more current than a partially charged battery. As a result, when selecting a proper C rating for the application, it is critical to consider the battery’s SOC.
- A lithium-ion battery’s C rating might degrade over time due to ageing and wear. As the battery is charged and discharged repeatedly, its internal resistance develops, decreasing its ability to supply high power.
High C Rating Benifits
- High C-rating batteries can produce a significant amount of power quickly, making them ideal for high-performance applications requiring rapid acceleration or continuous power production.
- High C rating batteries have lower internal resistance than low C rating batteries, which reduces voltage drop and improves battery efficiency.
- Because of their high power output, high C rating batteries may be charged quickly, minimising charging time and enhancing battery convenience.





The DCS LiFePO4 200ah Lithium Battery (Slim line) redefines power efficiency in a sleek design. Our 12v
200ah Lithium Ion Battery offers a high energy output and robust performance.