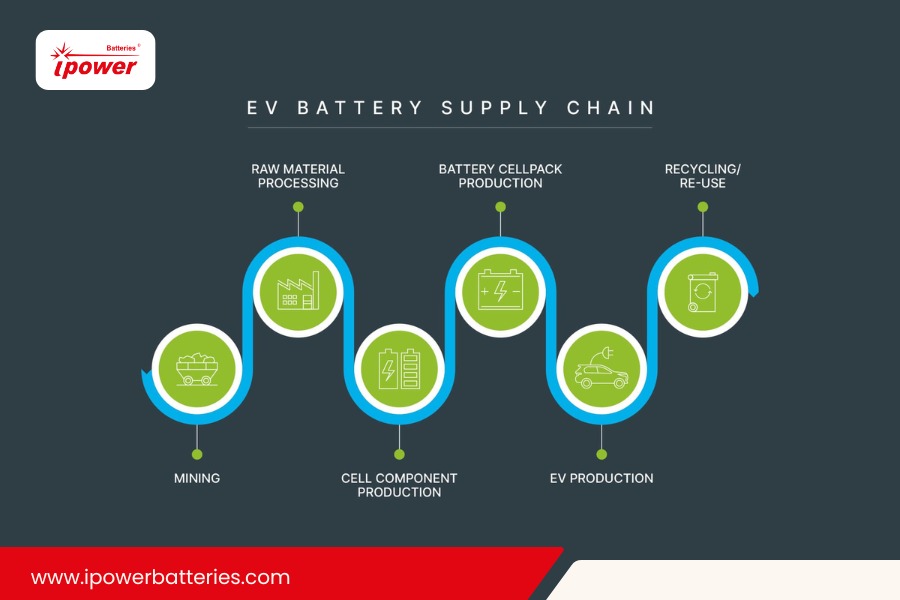
The electric vehicle (EV) industry is at the forefront of global efforts to decarbonize transportation, but its sustainability extends beyond just zero-emission driving. One of the most critical yet often overlooked aspects of the EV ecosystem is the sustainability of its battery supply chain. From raw material extraction to battery recycling, ensuring a sustainable supply chain is key to minimizing environmental impact, reducing costs, and securing long-term availability of essential materials.
Environmental Impact of EV Battery Production
Lithium-ion batteries, the backbone of EVs, require key raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite. Extracting these materials has significant environmental consequences, including deforestation, water contamination, and carbon emissions. Sustainable sourcing of these raw materials is essential to reducing the ecological footprint of EV production. Ethical mining practices, efficient resource extraction, and alternative material innovations can mitigate environmental damage while ensuring continued supply.
Ethical and Social Considerations
Many of the materials used in EV batteries come from regions with poor labor conditions and human rights violations. Cobalt mining in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), for example, has been linked to child labor and hazardous working conditions. Ensuring sustainability in the supply chain means adopting fair labor practices, enforcing corporate social responsibility (CSR) policies, and increasing transparency in sourcing. Initiatives like blockchain-based tracking systems and industry-wide certifications can help address these ethical concerns.
Geopolitical Risks and Supply Chain Resilience
The global battery supply chain is highly dependent on a few key regions for raw material extraction and processing. China dominates the lithium refining and battery manufacturing sector, while Africa and South America are major sources of raw materials. This concentration creates geopolitical risks and supply vulnerabilities. Diversifying sourcing strategies, developing domestic refining capabilities, and promoting circular economies through recycling can enhance supply chain resilience and reduce dependence on a single country or region.
The Role of Recycling and Second-Life Batteries
A sustainable battery supply chain must prioritize end-of-life solutions. Recycling spent EV batteries helps recover valuable materials, reducing the need for virgin resource extraction. Second-life applications, where EV batteries are repurposed for energy storage, further extend their lifecycle before recycling. Implementing robust recycling infrastructure and incentivizing manufacturers to adopt closed-loop systems are crucial for minimizing waste and optimizing material use.
Innovations in Sustainable Battery Technology
Advancements in battery chemistry and manufacturing techniques play a significant role in sustainability. Researchers are exploring alternatives to lithium-ion technology, such as solid-state batteries, sodium-ion batteries, and lithium-sulfur batteries, which promise improved energy efficiency and reduced reliance on scarce materials. Green manufacturing practices, including energy-efficient production processes and low-carbon battery production, also contribute to a more sustainable supply chain.
Policy and Industry Collaboration
Governments and industry stakeholders must work together to establish regulations and incentives for a greener EV battery supply chain. Policies like the European Union’s Battery Directive and the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act include provisions for responsible sourcing, sustainability reporting, and recycling mandates. Industry collaborations, such as partnerships between automakers and battery producers, can drive innovation and create more transparent, accountable supply chains.
The transition to electric mobility is a crucial step toward reducing global carbon emissions, but achieving true sustainability requires a holistic approach to the EV battery supply chain. From ethical sourcing and environmental conservation to recycling and technological advancements, every aspect of the supply chain must be optimized for long-term viability. By prioritizing sustainability, the global EV market can ensure a stable, responsible, and efficient battery ecosystem that supports the broader goals of clean transportation and environmental stewardship.