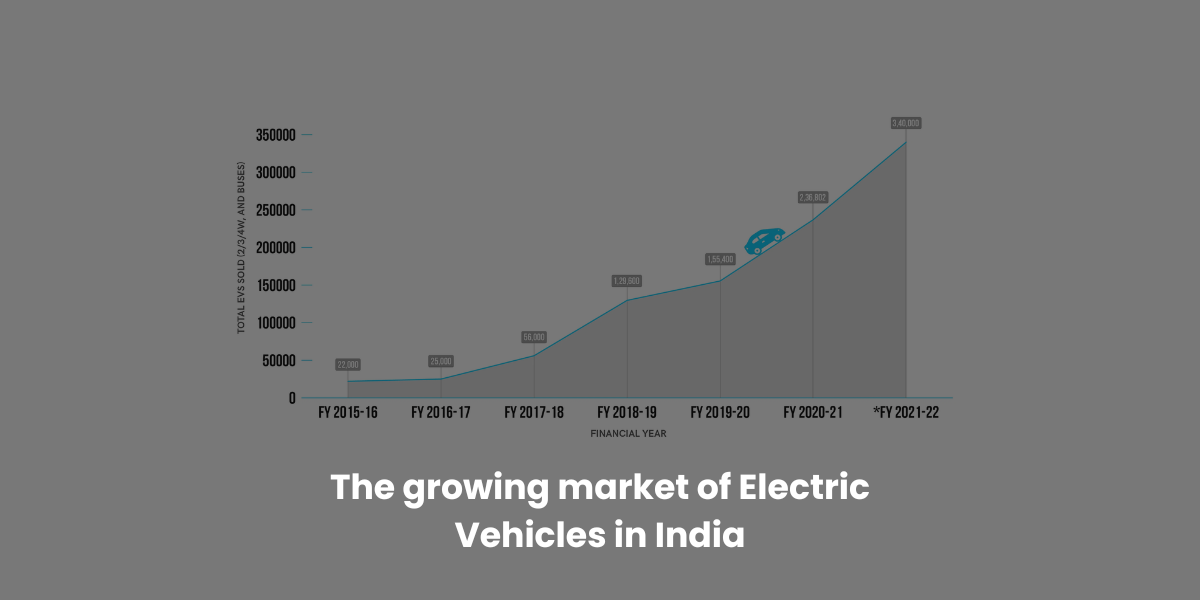
In recent years, there has been a substantial increase in the use of electric vehicles (EVs) in India. Because India is a major consumer of fossil fuels, the change to electric vehicles has multiple advantages for the environment, energy security, and the economy. In this blog article, we will look at the technological and legal implications of the EV boom in India.
Several technical considerations, including advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and government incentives, have contributed to India’s shift towards EVs.
Role of Battery Technology:
The invention of lithium-ion batteries was a changing point for the electric vehicle sector. These batteries are lighter, smaller, and have a higher energy density than standard lead-acid batteries. Lithium-ion batteries also have a lower self-discharge rate, which means they can hold a charge for longer periods of time. The advancement of battery technology has enabled electric vehicles to reach longer ranges, increasing their practicality for everyday use.
Role of Charging Infrastructure:
The availability of charging infrastructure is a crucial issue in electric vehicle adoption. In India, the government has initiated a number of steps to build a strong charging infrastructure. The FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles) scheme, for example, offers financial incentives for the installation of charging stations across the country. Several private companies have also entered the market to provide charging infrastructure, making electric vehicle owners more accessible.
Role of Government Incentives:
The Indian government has created a number of incentives to encourage the use of electric vehicles. The FAME scheme, for example, offers subsidies for the purchase of electric vehicles. The GST (Goods and Services Tax) for electric vehicles has also been slashed from 12% to 5% by the government. Furthermore, the federal government has waived road tax and registration fees for electric vehicles in numerous states, making them more cheap to consumers.
Now lets see how the electric vehicle market is impacting other sectors.
Impact of Environment:
The transition to electric vehicles has various environmental advantages. Electric vehicles release no harmful emissions like carbon monoxide or nitrogen oxides, which contribute to air pollution. Electric vehicle adoption could lower carbon emissions by up to 37% by 2030, according to a report by the Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers. The reduction in carbon emissions will also assist India in meeting its Paris Agreement goals.
Electric Vehicles helps in Energy Security:
India is heavily reliant on imported oil, which has serious consequences for the country’s energy security. Adoption of electric vehicles could lessen India’s reliance on imported oil, improving its energy security. Furthermore, electric vehicles may be charged using sustainable energy sources such as solar and wind power, reducing the country’s reliance on fossil fuels even further.
Economic Advantages:
The transition to electric vehicles provides various economic benefits for India. Adoption of electric vehicles, for example, might cut the country’s oil import cost, positively impacting its trade balance. Furthermore, the expansion of the electric car industry may result in the creation of new jobs in manufacturing, research, and development.
The growing popularity of electric vehicles in India has a number of technical and procedural ramifications. With advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure, as well as government incentives, electric vehicles have become more feasible and economical for consumers. The transition to electric vehicles provides various environmental, energy security, and economic benefits for India.
As the electric vehicle industry expands, it has the potential to revolutionise India’s energy landscape and contribute to the country’s long-term development goals.