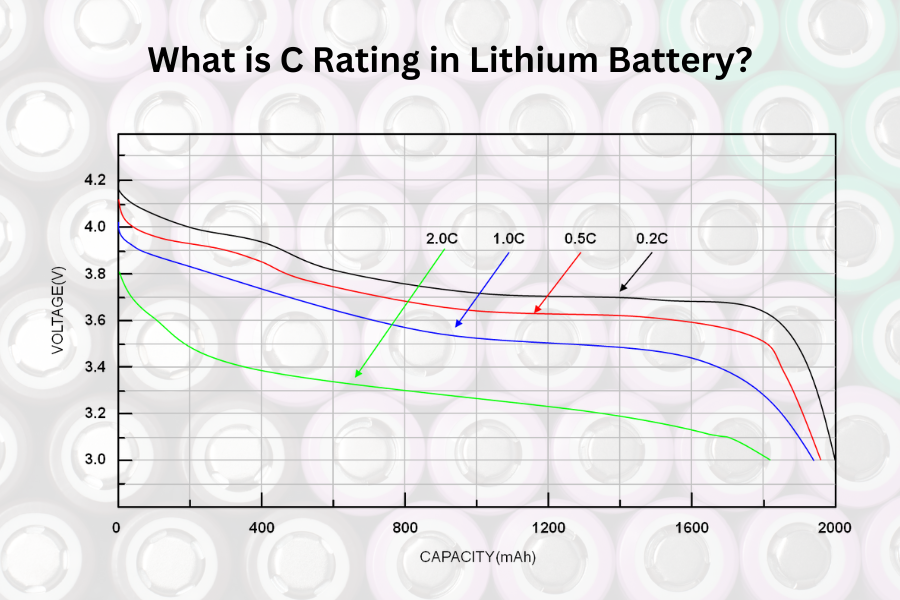
As the world continues its shift towards electrification, smart battery management systems (BMS) have emerged as indispensable tools for optimizing the performance, health, and efficiency of batteries. A smart BMS not only monitors the vital parameters of a battery but also provides a wealth of data that can be meticulously analyzed to gain insights into the battery’s condition. In this article, we delve into the spectrum of data that a smart BMS can offer, enabling us to decode the intricacies of battery health and efficiency.
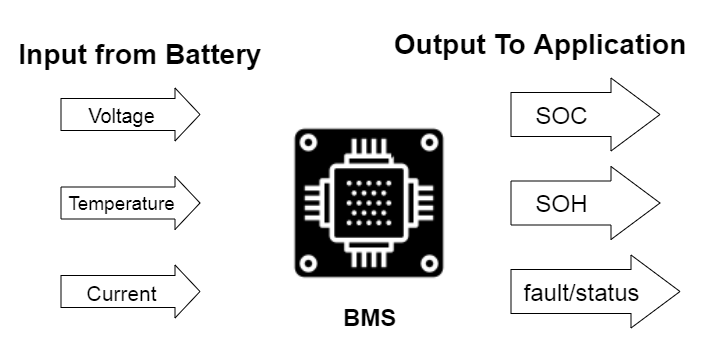
1 ) State of Charge (SOC)
- SOC is the amount of charge remaining in the battery expressed as a percentage of the total capacity.
- BMS continuously monitors SOC and provides real-time information to the driver or the vehicle’s control system.
- SOC data can help in predicting the remaining range of the vehicle and optimizing the charging and discharging cycles to prolong battery life.
2) State of Health (SOH)
- SOH is a measure of the battery’s health and capacity degradation over time.
- BMS can estimate SOH based on various factors such as the number of charge-discharge cycles, temperature, and operating conditions.
- SOH data can help in predicting the battery’s remaining lifespan and identifying any potential issues that may require maintenance or replacement.
3) Temperature
- Temperature is a critical parameter that affects the battery’s performance and lifespan.
- BMS continuously monitors the battery’s temperature and provides real-time information to the driver or the vehicle’s control system.
- Temperature data can help in optimizing the battery’s thermal management system and preventing overheating or undercooling.
4) Voltage
- Voltage is a measure of the battery’s electrical potential.
- BMS continuously monitors the battery’s voltage and provides real-time information to the driver or the vehicle’s control system.
- Voltage data can help in identifying any potential issues such as overcharging or undercharging and optimizing the charging and discharging cycles.
5) Charging and Discharging Cycles
- BMS records the number of charging and discharging cycles that the battery has undergone.
- Charging and discharging cycle data can help in estimating the battery’s remaining lifespan and identifying any potential issues that may require maintenance or replacement.
6) Energy Efficiency
- BMS can calculate the battery’s energy efficiency based on the amount of energy input and output.
- Energy efficiency data can help in optimizing the battery’s charging and discharging cycles and identifying any potential issues that may require maintenance or replacement.
7) Cell Balancing:
- Smart BMS systems manage individual cell voltages within a battery pack to ensure balanced charging and discharging.
- Cell balancing data reveals any disparities in cell performance, identifying cells that might be deteriorating faster than others.
- This data can guide maintenance decisions and improve overall pack longevity.
8) Charging and Discharging Efficiency:
- A BMS can offer insights into the battery’s charging and discharging efficiency, shedding light on energy losses during the processes.
- By comparing input and output energy, inefficiencies can be identified and corrected, enhancing overall energy utilization.
9) Predictive Maintenance:
- The data collected by a smart BMS allows for predictive maintenance. By analyzing trends and deviations from normal behavior, the system can forecast when maintenance might be needed, preventing potential failures and downtimes.
10) Fault Diagnostics:
- In case of anomalies or malfunctions, a BMS records data that can be used for diagnostic purposes.
- Analyzing this data helps identify the root causes of failures and aids in developing corrective measures.
In conclusion, the smart battery management system is a treasure trove of data that offers profound insights into a battery’s health, performance, and efficiency. By diligently analyzing this data, stakeholders can make informed decisions about battery maintenance, usage strategies, and replacement schedules. The integration of smart BMS technology is not only instrumental in extending battery life but also in promoting safer and more reliable applications across industries, from electric vehicles to renewable energy storage systems.